By Chelsea Rice, RDN, LDN
Metabolism is a term that’s often thrown around in the wellness industry, but what exactly is metabolism, and why does it matter? In this Metabolism 101 blog, we will dive into the world of metabolism, exploring what it is, how it works, how to test your metabolic rate, and how you can optimize it to support your overall well-being.
*Prefer to listen and learn? Check out our Metabolism podcast above or on your favorite platform!
What is your metabolism?
Metabolism refers to all the chemical processes that occur within your body to maintain life. It is the sum of all the reactions that take place to convert the food you eat into the energy and nutrients your body needs to function. Our bodies need this energy to do everything to stay alive- moving, thinking, growing, etc. Thousands of these chemical processes happen at the same time to keep our cells healthy and working properly.
How does your metabolism “work”?
After we eat food, the digestive system uses enzymes to break proteins down into amino acids, fats into fatty acids, and carbohydrates into glucose. These amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose are then absorbed into the blood, carried to the cells, and then can be released and used as energy by the body or stored in the body’s tissues.
In other words, your metabolism is a balance of:
- building up body tissues and energy stores (called anabolism)
- breaking down body tissues and energy stores to get more fuel for body functions (called catabolism)
Factors that can have an impact on your metabolism
Metabolism is a complicated chemical process, but there are a few things that may have an impact on your metabolism including:
- Body composition
- Muscle is an active tissue, while fat is an inactive tissue. This means that it takes more energy to build and maintain muscle than fat. People with higher muscle mass often have faster metabolisms.
- Lifestyle
- Your overall lifestyle may impact your body composition, which in turn can impact your metabolism. Lifestyle factors such as exercise routine, nutrition, sleep, and stress may all impact your metabolic rate.
- Gender and genetics
- Males tend to have faster metabolism than females, but that does not mean that is always the case. This is due to the fact that most men have more muscle mass, larger bones, and less body fat. The genes you inherit from your parents may also play a role, but it is important to remember that your current lifestyle your living has just as much of an impact.
- Age
- We often hear that your metabolism slows with age, but recent data suggests that our metabolism may not really start to decline until after the age of 60. Again, your lifestyle may impact your metabolism as you age, but in general, if you live an active/healthy lifestyle, you may not see your metabolism slow down as soon as you thought it would.
- Hormones
- Every metabolic function is impacted by your hormones. Examples of hormones that play a role in your metabolism include insulin, cortisol, leptin, ghrelin, testosterone, estrogen, thyroid hormones, growth hormone, and more.
Although there may be factors that are out of your control, it is important to remember that small lifestyle changes are what can have the biggest impact on your metabolism. Getting a good night of sleep (7-9 hours), incorporating strength training, eating a well balanced (high protein) diet, and managing stress are four of the most important lifestyle factors for your metabolism.
Want to learn more about your unique metabolism and personalized nutrition plan to help improve your metabolic function? Connect with Chelsea HERE.
Understanding your total daily energy expenditure
A lot of individuals think of metabolism as “how quickly you are burning calories in a day”. While this is true, as you can see from above your metabolism is a little more complicated than just that. But to keep it simple, let’s move onto talking about calories and your metabolic rate.
Your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the amount of energy used in a day. In other words, TDEE is the amount of total calories burned in a 24 hour period of time. TDEE is difficult to accurately measure, because it can fluctuate daily. Your TDEE is is comprised of four components:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) / Resting Metabolic Rate: BMR or RMR is the energy expended (calories burned) while at rest.
- Thermic Effect of Physical Activity: The more you move, the more calories you will burn in a day. With that being said, burning MORE calories while exercising does not make it a “better” workout. I always say “quality over quantity”. You want to ensure you are getting a good quality workout, instead of just focusing on the quantity of calories you are burning. Speak with a Registered Dietitian and Personal Trainer to learn more about the right type of physical activity for your wellness goals and nutritional intake.
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis: Energy expended for everything you do that does not include sleeping, eating, physical activity or exercise. For example, the calories you burn while fidgeting.
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): Chewing, swallowing, digesting, absorbing, and storing food also burns calories. Different foods have varying thermic effects; protein, for instance, requires more energy to digest than fats or carbohydrates.
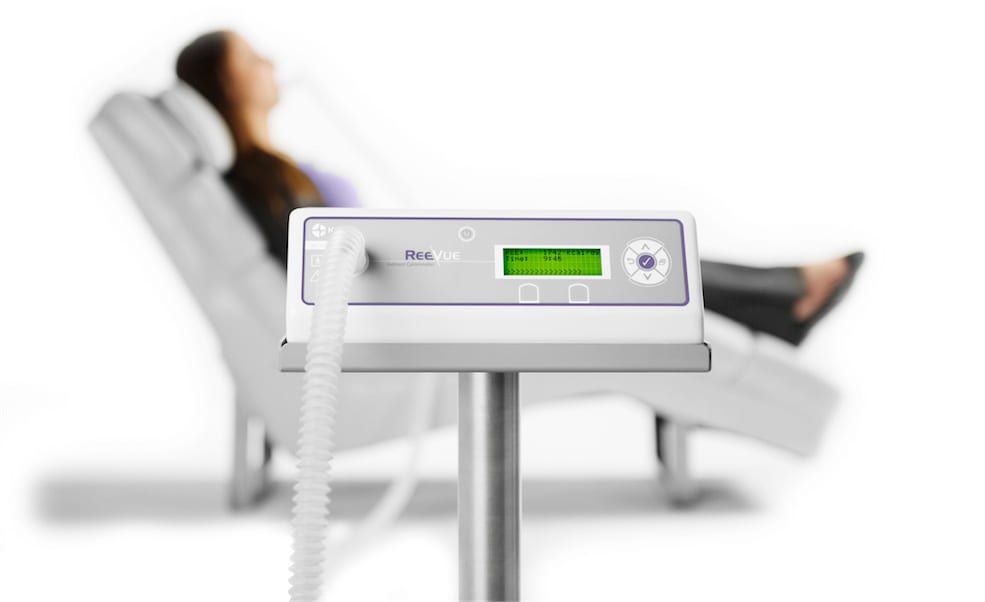
Metabolic Testing
One of the most common ways people estimate their metabolic rate is to use an online calculator or equation. Online calculators and equations are a good place to start, but if you want a more accurate understanding of your metabolic rate, I recommend taking a Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) test. Online calculators factor in your weight, height, age, sex, and exercise routine, while RMR tests involve actually breathing into a piece of equipment to help get data from inside your body instead of just using your metrics.
Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) testing measures your RMR with gas analysis (oxygen and carbon dioxide) through indirect calorimetry. In more simple terms, RMR testing is a quick, comfortable breathing test conducted while you are sitting or laying in a chair at rest.
To learn more about metabolic testing,
To find a Resting Metabolic Rate Testing Facility near you and learn more about metabolic testing, connect with Chelsea HERE.
Can I boost my metabolism?
The short answer….yes and no. While you can’t change your genetics or age, you can take steps to support a healthy metabolism through the years including:
- Eat a balanced diet (and ensure you are eating enough protein)
- Don’t skip meals
- Add in strength training into your exercise routine
- Get enough sleep (7-9 hours per night for adults)
- Manage your stress
Conclusion
Metabolism is a complex and vital process that influences your overall health and well-being. Understanding how it works and the factors that can affect it empowers you to make informed choices about your lifestyle, diet, and exercise habits. By adopting a balanced approach to these aspects of your life, you can optimize your metabolism and support a healthier, more energetic you. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, so it’s essential to find what works best for your body and needs.
Love this information but want to individualize your nutritional needs to your unique body?
Let’s connect and personalize it together! Get started HERE.